4C'S LEARNING CENTER
Be confident you're getting the best diamond for your money. Here you'll find unbiased information to help take the anxiety
out of this exciting time. We don't buy or sell diamonds and we don't get commissions for recommending certain retailers.
Be confident you're getting the best diamond for your money. Here you'll find unbiased information to help take the anxiety out of this exciting time. We don't buy or sell diamonds and we don't get commissions for recommending certain retailers.
4C's Color

Even though diamonds are considered colorless, most are shades of light yellow and brown. A diamond with no color at all is rare and ranks as the highest color grade - 'D'.
Diamonds are color graded on a scale from D (entirely colorless) to Z (noticeably yellowish or brownish). Color saturation gradually increases with each letter grade. The differences between grades are extremely subtle to the untrained eye but have a big impact on price. Read more about How Color Affects Price
Anything more than the 'Z' grade is considered a Fancy Color Diamond. Diamonds are found naturally in every color of the rainbow. Read more about Fancy Color Diamonds
Diamond Color Grading involves determining how little or how much body color is in a diamond. The less body color, the higher the grade; the more body color, the lower the grade. This process is about deciding the amount of color, or more accurately, the lack of color in a diamond.
What color diamond is the most popular?
Most people choose a diamond in the 'F' to 'K' color range.
Does the metal I choose for a ring affect the diamond's appearance?
Yes. Diamonds graded between 'D' to 'H' color look best when set in white metals such as platinum, palladium or white gold. Diamonds with more color, graded 'I-J' and lower, are best complemented by a yellow gold setting.
Why does the color scale start at the letter D?
If you're wondering why the scale starts at 'D' rather than 'A,' it's because it was common to sell diamonds as Triple A when the scale was introduced in 1953. To avoid any similarities with prior ratings that were arbitrary and inflated, the jewelry industry adopted a color scale from D to Z.
How are diamonds color graded?
Using special set of comparison diamonds, known as 'Masters', gemologists find the closest color match from among the Masters to the stone being graded. Each 'master' is the highest of each grade.
Diamonds are studied in the table-down (or bottom-up) position to determine the quantity of color. This means that graders view the diamond's pavilion and culet rather than its table or crown. Why? To eliminate interfering brilliance and glare coming from the diamond's top. Read more about Color Grading
What is the difference between a fancy yellow diamond and a 'bad' regular diamond?
The letter diamond color scale ends with 'Z', but color saturation doesn't stop at 'Z'; colors continue to increase in color and are considered Fancy Colored. Fancy Colored diamonds are graded on a broader scale that starts with 'Fancy Light', then just 'Fancy', then 'Fancy Intense' and lastly, the very rare 'Fancy Vivid'. We don't consider any diamond to be a 'bad' color, however, more common colors are the least costly and rare colors are the most costly. To understand how price relates to color grades, think of the entire color scale, from 'D' to 'Fancy Vivid' as a bell curve. The rarest and most costly diamonds - completely colorless and brightly colored - are at each end, and the more common slightly tinged diamonds - 'O' to 'S' - are in the middle.
Will my diamond change color as it ages?
No. The color of a diamond is stable and permanent. You can leave your diamond in the sun or boil it in cleaner - it will not change color.
The color of diamonds can only be changed by advanced methods such as exposure to intense radiation energy or heating to extreme temperatures, such as 2000&, while under tremendous pressure. These methods, known as treatments, are used on purpose to change or enhance the color of diamonds. If your diamond has undergone one of these treatments, then it must be disclosed by the jeweler and will be stated on your GCAL certificate. Read more about Diamond Treatments
D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M... What is the best diamond color for me?
When considering what color diamond is right for you, start by looking at an H or I color diamond. This is in the middle of the popular color grade range (from D to M color). If you see some color then consider buying a diamond of a higher color grade, and if you don't see any color then consider buying a diamond of a lower color grade.
It is difficult for an untrained eye to see the difference between each individual letter grade, but most people can easily see the distinction between diamonds of a few grade differences, such an E and an H or an H and a K, especially when compared side by side. Color differences are most noticeable when diamonds are next to one another. Keep this in mind when purchasing loose diamonds that will be set next to one another in a piece of jewelry. Make sure they are similar colors - not more than 2-3 grades different.
How do I know my diamond was graded correctly?
Make sure your diamond comes with a Grading certificate from a respected gemological laboratory, such as GCAL. GCAL is an independent laboratory, not affiliated with any jewelers, and has the consumers' best interests in mind.
Before GCAL gives a diamond its color grade, it is individually examined by two experts and verified by a third senior expert. GCAL's laboratory is a controlled environment, equipped with state-of-the-art instrumentation and lighting. There are only a handful of gemological laboratories in the world so well equipped.
In addition, GCAL uses only Precision Master Color diamonds for color grading comparison. Every diamond in each Precision Master Color set is specially selected because it is precisely the right color. GCAL examines thousands of diamonds to compile just one Precision Master Color set.
Although grading diamonds is an expert opinion and not an exact science, maintaining meticulous gemological tools, such as Precision Master Color sets, is one way that GCAL ensures the most accurate, objective and consistent grading possible. And don't forget... GCAL is the only diamond grading company to stand behind their grading with a money-backed grading guarantee. Read more about GCAL's Standards
Does fluorescence affect a diamond's color?
Yes, it can affect the appearance of color. The stronger the fluorescence the greater impact it has on the apparent color. Fluorescence that is graded as 'Faint' has little or no affect but 'Strong' fluorescence influences the appearance, especially in lighting environments with an intense UV component. But this influence is not always negative. For example, a diamond in the K to L range that is Faint Yellow will benefit from Medium Blue Fluorescence. Read more about Fluorescence
What causes the different colors of diamonds?
In theory, a diamond is pure carbon with a perfect atomic structure, but in the real world, this is extremely rare. On the atomic level, every diamond has some imperfections such as misaligned structure or, very commonly, impurities such as nitrogen and hydrogen. Nitrogen impurities cause yellow colors, boron impurities cause blue colors and structural imperfections cause pink and brown colors.
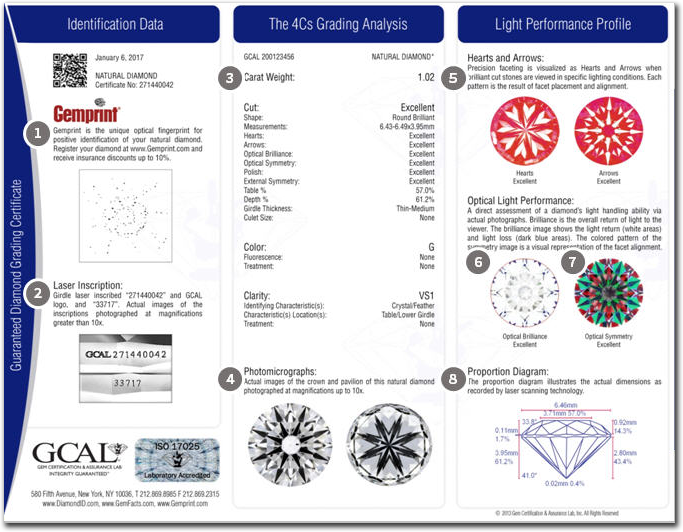
Each panel of a GCAL Certificate tells a story to the customer.
- Panel 1
Verifies the identification process
- Panel 2
Verifies the 4C's quality grading
- Panel 3
Illustrates the quality of cutting and proportions revealing the skill of the diamond cutter
- 1Gemprint
GEMPRINT
Gemprint
Gemprint® is a non-invasive, positive identification technology that records the unique optical 'fingerprint' of each diamond. Just like a human fingerprint, every diamond has a unique Gemprint. Capturing the unique Gemprint of your diamond in the initial processing stage, allows us to positively identify and track the diamond through our process. This optical fingerprint is captured and stored in GCAL's database for future verification and identification, and a digital image is printed on every GCAL Certificate.
How it works:
Gemprint uses a sophisticated system comprising laser technology, high resolution imaging, and automated positioning to direct a focused laser beam at the center of the diamond. The light enters the diamond and is broken into many rays as it reflects and refracts off the pavilion and crown facets. As the light reflects back out of the diamond, it creates a distinct Gemprint.
Laser Inscription
Laser Inscription quickly identifies a diamond and is included with this GCAL Guaranteed Diamond Grading Certificate. GCAL certified diamonds are laser inscribed with the unique certificate number assigned to the diamond. Photomicrographs, captured at more than 50x magnification, are taken to easily communicate what is inscribed on your diamond, and can be used as an additional piece of forensic identification of your diamond.
How it works:
GCAL uses a sophisticated IR laser technology specially designed for inscribing gemstones. When this laser is focused on a diamond's surface, it graphitizes a microscopic mark. A continuous series of these marks produces the numbers and letters you see on the girdle. The laser inscription mark is extremely shallow, only about 2-5 microns deep, less than one-tenth the width of the average human hair.
4Cs GRADING
WEIGHTS & MEASUREMENTS
Precise measurement of carat weight is important - slight differences can have a large impact on the value of a diamond. GCAL weighs diamonds on precise electronic balances according to international standards. This means that the weight is measured to the thousandth of a carat, and then is rounded to the hundredth of a carat. The electronic balances at GCAL are verified daily to ensure consistent and accurate results. The diamond is then measured by an optical scanning device that captures a series of high resolution images and creates an exact 3D model of every facet and angle, providing accurate geometrical measurements of the diamond. This proportion diagram appears on your GCAL certificate.
COLOR
Diamonds are color graded on a scale from D to Z. Each letter represents a slightly more saturated color. Your diamond is examined in a standard lighting environment and is compared to a set of Precision Master Color diamonds, which each have a precise color grade. Comparison of your diamond to the Precision Master diamonds continues until the color grade is determined. The difference between each color grade is very slight, but with experience, expert graders are able to consistently determine the accurate color grade of each diamond. GCAL utilizes a unique quality control procedure for grading the color and clarity of diamonds that assures the most accurate and consistent grading possible. At least three experienced gemologists examine and grade both the color and the clarity of every diamond. (After color grading, your diamond is checked for fluorescence, its reaction to ultraviolet light. A set of Master fluorescent diamonds is used to compare the strength of fluorescence. This intrinsic property is a permanent identifying characteristic of your diamond.)
CLARITY
Clarity is graded by examining your diamond under a microscope to assess internal and external characteristics such as crystals and feathers. A gemologist first inspects the diamond in the face-up position to find obvious inclusions. To find minute inclusions, the diamond has to be viewed through the pavilion as it is slowly rotated at least 3 full times, changing the viewing angle each time. The gemologist must assess the number, size, type, position and relief of each inclusion. After thorough inspection under the microscope, a 10x loupe is used to view the diamond in 4 different positions to determine the final clarity grade. GCAL utilizes a unique quality control procedure for grading the color and clarity of diamonds that assures the most accurate and consistent grading possible. At least three experienced gemologists examine and grade both the color and the clarity of every diamond.
RESEARCH
Before grading, every diamond is tested to confirm its origin - either natural earth mined or lab grown. If a diamond's origin cannot be verified by the initial spectroscopic analysis, then it is sent to the research department where additional more advanced tests are used to determine its authenticity. Considerable investment in state-of-the-art technologies has made GCAL one of the most well-equipped gem labs in the world. Once your diamond's origin is determined, it is ready for grading.
Photomicrograph
Photomicrographs are taken of the crown and pavilion of your diamond. These photos provide a forensic record of the exact appearance and condition of your diamond, and show internal and external characteristics visible at 10x magnification. Photographs are the most accurate way to illustrate the exact appearance and location of inclusions.
HEARTS & ARROWS
Hearts & Arrows is a term used to describe the patterns visible in perfectly faceted round brilliant cut diamonds when they are examined in specialized viewers. Through these viewers, it is possible to assess the alignment and consistency of every facet by looking at the equality of light return, or the hearts and arrows patterns.
A precisely faceted round brilliant diamond exhibits a pattern of eight arrows through the crown (top) side, and a pattern of eight hearts through the pavilion (bottom) side.
GCAL is the only laboratory that takes a real photograph of each diamond in the specialized viewer. This means that the images on your GCAL Certificate are actually of your diamond. Unlike the majority of the Hearts & Arrows photos printed on other lab reports or seen online, which are either generic sample images applied to every diamond or are computer generated - neither of which guarantees that the diamond you're paying a premium for is actually deserving of the term Hearts & Arrow.
OPTICAL BRILLIANCE
GCAL directly assesses the overall return of light to the viewer, called 'brilliance'.
The Optical Brilliance image is actually a digital photograph of the diamond taken in a special lighting environment that creates a strong contrast between the bright and dark areas. The image is then processed in a proprietary computer program that calculates the percentage of brilliance and the amount of light loss. This is a scientifically accurate and repeatable way to measure brilliance. The light gray areas of the image are facet outlines resulting from image processing to provide a realistic representation of the diamond's unique faceting.
In the Optical Brilliance Analysis image on the certificate, the white represents the light return and the blue represents areas of light loss. The light return is quantified based on measurable light return (aka - performance) and then graded as: Excellent, Very Good, Good, Fair or Poor.
Since the Optical Brilliance is measured by direct assessment, meaning that it is judged based on the way each diamond actually performs rather than a theoretical model, the brilliance image of each individual diamond will always look slightly different.
Brilliance is what gives a diamond its life, and what makes a diamond shine from across a room. Diamonds with a low percentage of brilliance look dull and dark.
OPTICAL SYMMETRY
The Optical Symmetry Analysis image is a digital photograph taken of each diamond in a special lighting environment that reveals the patterns of light return. All light returned at the same angles is represented by the same color. For example, all red areas represent light being returned within a consistent angle range. Therefore, the Optical Symmetry assesses the consistency of angles and alignment of facets by looking at the equality of light return.
Since the Optical Symmetry is measured by direct assessment, meaning that it is judged based on the way each diamond actually performs rather than a theoretical model, the symmetry images of each individual diamond will always look slightly different. Like the beauty and ever changing color patterns in a kaleidoscope, each diamond reveals its unique reflective pattern of symmetry. You can judge the cut of a diamond yourself simply by examining the symmetry image-the more even the pattern, the better the symmetry
PROPORTION DIAGRAM
Each diamond is measured by an optical scanning device that captures a series of high resolution images and creates an exact 3D model of every facet and angle, providing accurate geometrical measurements of the diamond. This proportion diagram appears on your GCAL certificate.
- 2Laser Inscription
Laser Inscription
Gemprint
Gemprint® is a non-invasive, positive identification technology that records the unique optical 'fingerprint' of each diamond. Just like a human fingerprint, every diamond has a unique Gemprint. Capturing the unique Gemprint of your diamond in the initial processing stage, allows us to positively identify and track the diamond through our process. This optical fingerprint is captured and stored in GCAL's database for future verification and identification, and a digital image is printed on every GCAL Certificate.
How it works:
Gemprint uses a sophisticated system comprising laser technology, high resolution imaging, and automated positioning to direct a focused laser beam at the center of the diamond. The light enters the diamond and is broken into many rays as it reflects and refracts off the pavilion and crown facets. As the light reflects back out of the diamond, it creates a distinct Gemprint.
Laser Inscription
Laser Inscription quickly identifies a diamond and is included with this GCAL Guaranteed Diamond Grading Certificate. GCAL certified diamonds are laser inscribed with the unique certificate number assigned to the diamond. Photomicrographs, captured at more than 50x magnification, are taken to easily communicate what is inscribed on your diamond, and can be used as an additional piece of forensic identification of your diamond.
How it works:
GCAL uses a sophisticated IR laser technology specially designed for inscribing gemstones. When this laser is focused on a diamond's surface, it graphitizes a microscopic mark. A continuous series of these marks produces the numbers and letters you see on the girdle. The laser inscription mark is extremely shallow, only about 2-5 microns deep, less than one-tenth the width of the average human hair.
4Cs GRADING
WEIGHTS & MEASUREMENTS
Precise measurement of carat weight is important - slight differences can have a large impact on the value of a diamond. GCAL weighs diamonds on precise electronic balances according to international standards. This means that the weight is measured to the thousandth of a carat, and then is rounded to the hundredth of a carat. The electronic balances at GCAL are verified daily to ensure consistent and accurate results. The diamond is then measured by an optical scanning device that captures a series of high resolution images and creates an exact 3D model of every facet and angle, providing accurate geometrical measurements of the diamond. This proportion diagram appears on your GCAL certificate.
COLOR
Diamonds are color graded on a scale from D to Z. Each letter represents a slightly more saturated color. Your diamond is examined in a standard lighting environment and is compared to a set of Precision Master Color diamonds, which each have a precise color grade. Comparison of your diamond to the Precision Master diamonds continues until the color grade is determined. The difference between each color grade is very slight, but with experience, expert graders are able to consistently determine the accurate color grade of each diamond. GCAL utilizes a unique quality control procedure for grading the color and clarity of diamonds that assures the most accurate and consistent grading possible. At least three experienced gemologists examine and grade both the color and the clarity of every diamond. (After color grading, your diamond is checked for fluorescence, its reaction to ultraviolet light. A set of Master fluorescent diamonds is used to compare the strength of fluorescence. This intrinsic property is a permanent identifying characteristic of your diamond.)
CLARITY
Clarity is graded by examining your diamond under a microscope to assess internal and external characteristics such as crystals and feathers. A gemologist first inspects the diamond in the face-up position to find obvious inclusions. To find minute inclusions, the diamond has to be viewed through the pavilion as it is slowly rotated at least 3 full times, changing the viewing angle each time. The gemologist must assess the number, size, type, position and relief of each inclusion. After thorough inspection under the microscope, a 10x loupe is used to view the diamond in 4 different positions to determine the final clarity grade. GCAL utilizes a unique quality control procedure for grading the color and clarity of diamonds that assures the most accurate and consistent grading possible. At least three experienced gemologists examine and grade both the color and the clarity of every diamond.
RESEARCH
Before grading, every diamond is tested to confirm its origin - either natural earth mined or lab grown. If a diamond's origin cannot be verified by the initial spectroscopic analysis, then it is sent to the research department where additional more advanced tests are used to determine its authenticity. Considerable investment in state-of-the-art technologies has made GCAL one of the most well-equipped gem labs in the world. Once your diamond's origin is determined, it is ready for grading.
Photomicrograph
Photomicrographs are taken of the crown and pavilion of your diamond. These photos provide a forensic record of the exact appearance and condition of your diamond, and show internal and external characteristics visible at 10x magnification. Photographs are the most accurate way to illustrate the exact appearance and location of inclusions.
HEARTS & ARROWS
Hearts & Arrows is a term used to describe the patterns visible in perfectly faceted round brilliant cut diamonds when they are examined in specialized viewers. Through these viewers, it is possible to assess the alignment and consistency of every facet by looking at the equality of light return, or the hearts and arrows patterns.
A precisely faceted round brilliant diamond exhibits a pattern of eight arrows through the crown (top) side, and a pattern of eight hearts through the pavilion (bottom) side.
GCAL is the only laboratory that takes a real photograph of each diamond in the specialized viewer. This means that the images on your GCAL Certificate are actually of your diamond. Unlike the majority of the Hearts & Arrows photos printed on other lab reports or seen online, which are either generic sample images applied to every diamond or are computer generated - neither of which guarantees that the diamond you're paying a premium for is actually deserving of the term Hearts & Arrow.
OPTICAL BRILLIANCE
GCAL directly assesses the overall return of light to the viewer, called 'brilliance'.
The Optical Brilliance image is actually a digital photograph of the diamond taken in a special lighting environment that creates a strong contrast between the bright and dark areas. The image is then processed in a proprietary computer program that calculates the percentage of brilliance and the amount of light loss. This is a scientifically accurate and repeatable way to measure brilliance. The light gray areas of the image are facet outlines resulting from image processing to provide a realistic representation of the diamond's unique faceting.
In the Optical Brilliance Analysis image on the certificate, the white represents the light return and the blue represents areas of light loss. The light return is quantified based on measurable light return (aka - performance) and then graded as: Excellent, Very Good, Good, Fair or Poor.
Since the Optical Brilliance is measured by direct assessment, meaning that it is judged based on the way each diamond actually performs rather than a theoretical model, the brilliance image of each individual diamond will always look slightly different.
Brilliance is what gives a diamond its life, and what makes a diamond shine from across a room. Diamonds with a low percentage of brilliance look dull and dark.
OPTICAL SYMMETRY
The Optical Symmetry Analysis image is a digital photograph taken of each diamond in a special lighting environment that reveals the patterns of light return. All light returned at the same angles is represented by the same color. For example, all red areas represent light being returned within a consistent angle range. Therefore, the Optical Symmetry assesses the consistency of angles and alignment of facets by looking at the equality of light return.
Since the Optical Symmetry is measured by direct assessment, meaning that it is judged based on the way each diamond actually performs rather than a theoretical model, the symmetry images of each individual diamond will always look slightly different. Like the beauty and ever changing color patterns in a kaleidoscope, each diamond reveals its unique reflective pattern of symmetry. You can judge the cut of a diamond yourself simply by examining the symmetry image-the more even the pattern, the better the symmetry
PROPORTION DIAGRAM
Each diamond is measured by an optical scanning device that captures a series of high resolution images and creates an exact 3D model of every facet and angle, providing accurate geometrical measurements of the diamond. This proportion diagram appears on your GCAL certificate.
- 34C's Grading
4C's Grading
Gemprint
Gemprint® is a non-invasive, positive identification technology that records the unique optical 'fingerprint' of each diamond. Just like a human fingerprint, every diamond has a unique Gemprint. Capturing the unique Gemprint of your diamond in the initial processing stage, allows us to positively identify and track the diamond through our process. This optical fingerprint is captured and stored in GCAL's database for future verification and identification, and a digital image is printed on every GCAL Certificate.
How it works:
Gemprint uses a sophisticated system comprising laser technology, high resolution imaging, and automated positioning to direct a focused laser beam at the center of the diamond. The light enters the diamond and is broken into many rays as it reflects and refracts off the pavilion and crown facets. As the light reflects back out of the diamond, it creates a distinct Gemprint.
Laser Inscription
Laser Inscription quickly identifies a diamond and is included with this GCAL Guaranteed Diamond Grading Certificate. GCAL certified diamonds are laser inscribed with the unique certificate number assigned to the diamond. Photomicrographs, captured at more than 50x magnification, are taken to easily communicate what is inscribed on your diamond, and can be used as an additional piece of forensic identification of your diamond.
How it works:
GCAL uses a sophisticated IR laser technology specially designed for inscribing gemstones. When this laser is focused on a diamond's surface, it graphitizes a microscopic mark. A continuous series of these marks produces the numbers and letters you see on the girdle. The laser inscription mark is extremely shallow, only about 2-5 microns deep, less than one-tenth the width of the average human hair.
4Cs GRADING
WEIGHTS & MEASUREMENTS
Precise measurement of carat weight is important - slight differences can have a large impact on the value of a diamond. GCAL weighs diamonds on precise electronic balances according to international standards. This means that the weight is measured to the thousandth of a carat, and then is rounded to the hundredth of a carat. The electronic balances at GCAL are verified daily to ensure consistent and accurate results. The diamond is then measured by an optical scanning device that captures a series of high resolution images and creates an exact 3D model of every facet and angle, providing accurate geometrical measurements of the diamond. This proportion diagram appears on your GCAL certificate.
COLOR
Diamonds are color graded on a scale from D to Z. Each letter represents a slightly more saturated color. Your diamond is examined in a standard lighting environment and is compared to a set of Precision Master Color diamonds, which each have a precise color grade. Comparison of your diamond to the Precision Master diamonds continues until the color grade is determined. The difference between each color grade is very slight, but with experience, expert graders are able to consistently determine the accurate color grade of each diamond. GCAL utilizes a unique quality control procedure for grading the color and clarity of diamonds that assures the most accurate and consistent grading possible. At least three experienced gemologists examine and grade both the color and the clarity of every diamond. (After color grading, your diamond is checked for fluorescence, its reaction to ultraviolet light. A set of Master fluorescent diamonds is used to compare the strength of fluorescence. This intrinsic property is a permanent identifying characteristic of your diamond.)
CLARITY
Clarity is graded by examining your diamond under a microscope to assess internal and external characteristics such as crystals and feathers. A gemologist first inspects the diamond in the face-up position to find obvious inclusions. To find minute inclusions, the diamond has to be viewed through the pavilion as it is slowly rotated at least 3 full times, changing the viewing angle each time. The gemologist must assess the number, size, type, position and relief of each inclusion. After thorough inspection under the microscope, a 10x loupe is used to view the diamond in 4 different positions to determine the final clarity grade. GCAL utilizes a unique quality control procedure for grading the color and clarity of diamonds that assures the most accurate and consistent grading possible. At least three experienced gemologists examine and grade both the color and the clarity of every diamond.
RESEARCH
Before grading, every diamond is tested to confirm its origin - either natural earth mined or lab grown. If a diamond's origin cannot be verified by the initial spectroscopic analysis, then it is sent to the research department where additional more advanced tests are used to determine its authenticity. Considerable investment in state-of-the-art technologies has made GCAL one of the most well-equipped gem labs in the world. Once your diamond's origin is determined, it is ready for grading.
Photomicrograph
Photomicrographs are taken of the crown and pavilion of your diamond. These photos provide a forensic record of the exact appearance and condition of your diamond, and show internal and external characteristics visible at 10x magnification. Photographs are the most accurate way to illustrate the exact appearance and location of inclusions.
HEARTS & ARROWS
Hearts & Arrows is a term used to describe the patterns visible in perfectly faceted round brilliant cut diamonds when they are examined in specialized viewers. Through these viewers, it is possible to assess the alignment and consistency of every facet by looking at the equality of light return, or the hearts and arrows patterns.
A precisely faceted round brilliant diamond exhibits a pattern of eight arrows through the crown (top) side, and a pattern of eight hearts through the pavilion (bottom) side.
GCAL is the only laboratory that takes a real photograph of each diamond in the specialized viewer. This means that the images on your GCAL Certificate are actually of your diamond. Unlike the majority of the Hearts & Arrows photos printed on other lab reports or seen online, which are either generic sample images applied to every diamond or are computer generated - neither of which guarantees that the diamond you're paying a premium for is actually deserving of the term Hearts & Arrow.
OPTICAL BRILLIANCE
GCAL directly assesses the overall return of light to the viewer, called 'brilliance'.
The Optical Brilliance image is actually a digital photograph of the diamond taken in a special lighting environment that creates a strong contrast between the bright and dark areas. The image is then processed in a proprietary computer program that calculates the percentage of brilliance and the amount of light loss. This is a scientifically accurate and repeatable way to measure brilliance. The light gray areas of the image are facet outlines resulting from image processing to provide a realistic representation of the diamond's unique faceting.
In the Optical Brilliance Analysis image on the certificate, the white represents the light return and the blue represents areas of light loss. The light return is quantified based on measurable light return (aka - performance) and then graded as: Excellent, Very Good, Good, Fair or Poor.
Since the Optical Brilliance is measured by direct assessment, meaning that it is judged based on the way each diamond actually performs rather than a theoretical model, the brilliance image of each individual diamond will always look slightly different.
Brilliance is what gives a diamond its life, and what makes a diamond shine from across a room. Diamonds with a low percentage of brilliance look dull and dark.
OPTICAL SYMMETRY
The Optical Symmetry Analysis image is a digital photograph taken of each diamond in a special lighting environment that reveals the patterns of light return. All light returned at the same angles is represented by the same color. For example, all red areas represent light being returned within a consistent angle range. Therefore, the Optical Symmetry assesses the consistency of angles and alignment of facets by looking at the equality of light return.
Since the Optical Symmetry is measured by direct assessment, meaning that it is judged based on the way each diamond actually performs rather than a theoretical model, the symmetry images of each individual diamond will always look slightly different. Like the beauty and ever changing color patterns in a kaleidoscope, each diamond reveals its unique reflective pattern of symmetry. You can judge the cut of a diamond yourself simply by examining the symmetry image-the more even the pattern, the better the symmetry
PROPORTION DIAGRAM
Each diamond is measured by an optical scanning device that captures a series of high resolution images and creates an exact 3D model of every facet and angle, providing accurate geometrical measurements of the diamond. This proportion diagram appears on your GCAL certificate.
- 4Photomicrograph
Photomicrograph
Gemprint
Gemprint® is a non-invasive, positive identification technology that records the unique optical 'fingerprint' of each diamond. Just like a human fingerprint, every diamond has a unique Gemprint. Capturing the unique Gemprint of your diamond in the initial processing stage, allows us to positively identify and track the diamond through our process. This optical fingerprint is captured and stored in GCAL's database for future verification and identification, and a digital image is printed on every GCAL Certificate.
How it works:
Gemprint uses a sophisticated system comprising laser technology, high resolution imaging, and automated positioning to direct a focused laser beam at the center of the diamond. The light enters the diamond and is broken into many rays as it reflects and refracts off the pavilion and crown facets. As the light reflects back out of the diamond, it creates a distinct Gemprint.
Laser Inscription
Laser Inscription quickly identifies a diamond and is included with this GCAL Guaranteed Diamond Grading Certificate. GCAL certified diamonds are laser inscribed with the unique certificate number assigned to the diamond. Photomicrographs, captured at more than 50x magnification, are taken to easily communicate what is inscribed on your diamond, and can be used as an additional piece of forensic identification of your diamond.
How it works:
GCAL uses a sophisticated IR laser technology specially designed for inscribing gemstones. When this laser is focused on a diamond's surface, it graphitizes a microscopic mark. A continuous series of these marks produces the numbers and letters you see on the girdle. The laser inscription mark is extremely shallow, only about 2-5 microns deep, less than one-tenth the width of the average human hair.
4Cs GRADING
WEIGHTS & MEASUREMENTS
Precise measurement of carat weight is important - slight differences can have a large impact on the value of a diamond. GCAL weighs diamonds on precise electronic balances according to international standards. This means that the weight is measured to the thousandth of a carat, and then is rounded to the hundredth of a carat. The electronic balances at GCAL are verified daily to ensure consistent and accurate results. The diamond is then measured by an optical scanning device that captures a series of high resolution images and creates an exact 3D model of every facet and angle, providing accurate geometrical measurements of the diamond. This proportion diagram appears on your GCAL certificate.
COLOR
Diamonds are color graded on a scale from D to Z. Each letter represents a slightly more saturated color. Your diamond is examined in a standard lighting environment and is compared to a set of Precision Master Color diamonds, which each have a precise color grade. Comparison of your diamond to the Precision Master diamonds continues until the color grade is determined. The difference between each color grade is very slight, but with experience, expert graders are able to consistently determine the accurate color grade of each diamond. GCAL utilizes a unique quality control procedure for grading the color and clarity of diamonds that assures the most accurate and consistent grading possible. At least three experienced gemologists examine and grade both the color and the clarity of every diamond. (After color grading, your diamond is checked for fluorescence, its reaction to ultraviolet light. A set of Master fluorescent diamonds is used to compare the strength of fluorescence. This intrinsic property is a permanent identifying characteristic of your diamond.)
CLARITY
Clarity is graded by examining your diamond under a microscope to assess internal and external characteristics such as crystals and feathers. A gemologist first inspects the diamond in the face-up position to find obvious inclusions. To find minute inclusions, the diamond has to be viewed through the pavilion as it is slowly rotated at least 3 full times, changing the viewing angle each time. The gemologist must assess the number, size, type, position and relief of each inclusion. After thorough inspection under the microscope, a 10x loupe is used to view the diamond in 4 different positions to determine the final clarity grade. GCAL utilizes a unique quality control procedure for grading the color and clarity of diamonds that assures the most accurate and consistent grading possible. At least three experienced gemologists examine and grade both the color and the clarity of every diamond.
RESEARCH
Before grading, every diamond is tested to confirm its origin - either natural earth mined or lab grown. If a diamond's origin cannot be verified by the initial spectroscopic analysis, then it is sent to the research department where additional more advanced tests are used to determine its authenticity. Considerable investment in state-of-the-art technologies has made GCAL one of the most well-equipped gem labs in the world. Once your diamond's origin is determined, it is ready for grading.
Photomicrograph
Photomicrographs are taken of the crown and pavilion of your diamond. These photos provide a forensic record of the exact appearance and condition of your diamond, and show internal and external characteristics visible at 10x magnification. Photographs are the most accurate way to illustrate the exact appearance and location of inclusions.
HEARTS & ARROWS
Hearts & Arrows is a term used to describe the patterns visible in perfectly faceted round brilliant cut diamonds when they are examined in specialized viewers. Through these viewers, it is possible to assess the alignment and consistency of every facet by looking at the equality of light return, or the hearts and arrows patterns.
A precisely faceted round brilliant diamond exhibits a pattern of eight arrows through the crown (top) side, and a pattern of eight hearts through the pavilion (bottom) side.
GCAL is the only laboratory that takes a real photograph of each diamond in the specialized viewer. This means that the images on your GCAL Certificate are actually of your diamond. Unlike the majority of the Hearts & Arrows photos printed on other lab reports or seen online, which are either generic sample images applied to every diamond or are computer generated - neither of which guarantees that the diamond you're paying a premium for is actually deserving of the term Hearts & Arrow.
OPTICAL BRILLIANCE
GCAL directly assesses the overall return of light to the viewer, called 'brilliance'.
The Optical Brilliance image is actually a digital photograph of the diamond taken in a special lighting environment that creates a strong contrast between the bright and dark areas. The image is then processed in a proprietary computer program that calculates the percentage of brilliance and the amount of light loss. This is a scientifically accurate and repeatable way to measure brilliance. The light gray areas of the image are facet outlines resulting from image processing to provide a realistic representation of the diamond's unique faceting.
In the Optical Brilliance Analysis image on the certificate, the white represents the light return and the blue represents areas of light loss. The light return is quantified based on measurable light return (aka - performance) and then graded as: Excellent, Very Good, Good, Fair or Poor.
Since the Optical Brilliance is measured by direct assessment, meaning that it is judged based on the way each diamond actually performs rather than a theoretical model, the brilliance image of each individual diamond will always look slightly different.
Brilliance is what gives a diamond its life, and what makes a diamond shine from across a room. Diamonds with a low percentage of brilliance look dull and dark.
OPTICAL SYMMETRY
The Optical Symmetry Analysis image is a digital photograph taken of each diamond in a special lighting environment that reveals the patterns of light return. All light returned at the same angles is represented by the same color. For example, all red areas represent light being returned within a consistent angle range. Therefore, the Optical Symmetry assesses the consistency of angles and alignment of facets by looking at the equality of light return.
Since the Optical Symmetry is measured by direct assessment, meaning that it is judged based on the way each diamond actually performs rather than a theoretical model, the symmetry images of each individual diamond will always look slightly different. Like the beauty and ever changing color patterns in a kaleidoscope, each diamond reveals its unique reflective pattern of symmetry. You can judge the cut of a diamond yourself simply by examining the symmetry image-the more even the pattern, the better the symmetry
PROPORTION DIAGRAM
Each diamond is measured by an optical scanning device that captures a series of high resolution images and creates an exact 3D model of every facet and angle, providing accurate geometrical measurements of the diamond. This proportion diagram appears on your GCAL certificate.
- 5Hearts & Arrow
Hearts & Arrow
Gemprint
Gemprint® is a non-invasive, positive identification technology that records the unique optical 'fingerprint' of each diamond. Just like a human fingerprint, every diamond has a unique Gemprint. Capturing the unique Gemprint of your diamond in the initial processing stage, allows us to positively identify and track the diamond through our process. This optical fingerprint is captured and stored in GCAL's database for future verification and identification, and a digital image is printed on every GCAL Certificate.
How it works:
Gemprint uses a sophisticated system comprising laser technology, high resolution imaging, and automated positioning to direct a focused laser beam at the center of the diamond. The light enters the diamond and is broken into many rays as it reflects and refracts off the pavilion and crown facets. As the light reflects back out of the diamond, it creates a distinct Gemprint.
Laser Inscription
Laser Inscription quickly identifies a diamond and is included with this GCAL Guaranteed Diamond Grading Certificate. GCAL certified diamonds are laser inscribed with the unique certificate number assigned to the diamond. Photomicrographs, captured at more than 50x magnification, are taken to easily communicate what is inscribed on your diamond, and can be used as an additional piece of forensic identification of your diamond.
How it works:
GCAL uses a sophisticated IR laser technology specially designed for inscribing gemstones. When this laser is focused on a diamond's surface, it graphitizes a microscopic mark. A continuous series of these marks produces the numbers and letters you see on the girdle. The laser inscription mark is extremely shallow, only about 2-5 microns deep, less than one-tenth the width of the average human hair.
4Cs GRADING
WEIGHTS & MEASUREMENTS
Precise measurement of carat weight is important - slight differences can have a large impact on the value of a diamond. GCAL weighs diamonds on precise electronic balances according to international standards. This means that the weight is measured to the thousandth of a carat, and then is rounded to the hundredth of a carat. The electronic balances at GCAL are verified daily to ensure consistent and accurate results. The diamond is then measured by an optical scanning device that captures a series of high resolution images and creates an exact 3D model of every facet and angle, providing accurate geometrical measurements of the diamond. This proportion diagram appears on your GCAL certificate.
COLOR
Diamonds are color graded on a scale from D to Z. Each letter represents a slightly more saturated color. Your diamond is examined in a standard lighting environment and is compared to a set of Precision Master Color diamonds, which each have a precise color grade. Comparison of your diamond to the Precision Master diamonds continues until the color grade is determined. The difference between each color grade is very slight, but with experience, expert graders are able to consistently determine the accurate color grade of each diamond. GCAL utilizes a unique quality control procedure for grading the color and clarity of diamonds that assures the most accurate and consistent grading possible. At least three experienced gemologists examine and grade both the color and the clarity of every diamond. (After color grading, your diamond is checked for fluorescence, its reaction to ultraviolet light. A set of Master fluorescent diamonds is used to compare the strength of fluorescence. This intrinsic property is a permanent identifying characteristic of your diamond.)
CLARITY
Clarity is graded by examining your diamond under a microscope to assess internal and external characteristics such as crystals and feathers. A gemologist first inspects the diamond in the face-up position to find obvious inclusions. To find minute inclusions, the diamond has to be viewed through the pavilion as it is slowly rotated at least 3 full times, changing the viewing angle each time. The gemologist must assess the number, size, type, position and relief of each inclusion. After thorough inspection under the microscope, a 10x loupe is used to view the diamond in 4 different positions to determine the final clarity grade. GCAL utilizes a unique quality control procedure for grading the color and clarity of diamonds that assures the most accurate and consistent grading possible. At least three experienced gemologists examine and grade both the color and the clarity of every diamond.
RESEARCH
Before grading, every diamond is tested to confirm its origin - either natural earth mined or lab grown. If a diamond's origin cannot be verified by the initial spectroscopic analysis, then it is sent to the research department where additional more advanced tests are used to determine its authenticity. Considerable investment in state-of-the-art technologies has made GCAL one of the most well-equipped gem labs in the world. Once your diamond's origin is determined, it is ready for grading.
Photomicrograph
Photomicrographs are taken of the crown and pavilion of your diamond. These photos provide a forensic record of the exact appearance and condition of your diamond, and show internal and external characteristics visible at 10x magnification. Photographs are the most accurate way to illustrate the exact appearance and location of inclusions.
HEARTS & ARROWS
Hearts & Arrows is a term used to describe the patterns visible in perfectly faceted round brilliant cut diamonds when they are examined in specialized viewers. Through these viewers, it is possible to assess the alignment and consistency of every facet by looking at the equality of light return, or the hearts and arrows patterns.
A precisely faceted round brilliant diamond exhibits a pattern of eight arrows through the crown (top) side, and a pattern of eight hearts through the pavilion (bottom) side.
GCAL is the only laboratory that takes a real photograph of each diamond in the specialized viewer. This means that the images on your GCAL Certificate are actually of your diamond. Unlike the majority of the Hearts & Arrows photos printed on other lab reports or seen online, which are either generic sample images applied to every diamond or are computer generated - neither of which guarantees that the diamond you're paying a premium for is actually deserving of the term Hearts & Arrow.
OPTICAL BRILLIANCE
GCAL directly assesses the overall return of light to the viewer, called 'brilliance'.
The Optical Brilliance image is actually a digital photograph of the diamond taken in a special lighting environment that creates a strong contrast between the bright and dark areas. The image is then processed in a proprietary computer program that calculates the percentage of brilliance and the amount of light loss. This is a scientifically accurate and repeatable way to measure brilliance. The light gray areas of the image are facet outlines resulting from image processing to provide a realistic representation of the diamond's unique faceting.
In the Optical Brilliance Analysis image on the certificate, the white represents the light return and the blue represents areas of light loss. The light return is quantified based on measurable light return (aka - performance) and then graded as: Excellent, Very Good, Good, Fair or Poor.
Since the Optical Brilliance is measured by direct assessment, meaning that it is judged based on the way each diamond actually performs rather than a theoretical model, the brilliance image of each individual diamond will always look slightly different.
Brilliance is what gives a diamond its life, and what makes a diamond shine from across a room. Diamonds with a low percentage of brilliance look dull and dark.
OPTICAL SYMMETRY
The Optical Symmetry Analysis image is a digital photograph taken of each diamond in a special lighting environment that reveals the patterns of light return. All light returned at the same angles is represented by the same color. For example, all red areas represent light being returned within a consistent angle range. Therefore, the Optical Symmetry assesses the consistency of angles and alignment of facets by looking at the equality of light return.
Since the Optical Symmetry is measured by direct assessment, meaning that it is judged based on the way each diamond actually performs rather than a theoretical model, the symmetry images of each individual diamond will always look slightly different. Like the beauty and ever changing color patterns in a kaleidoscope, each diamond reveals its unique reflective pattern of symmetry. You can judge the cut of a diamond yourself simply by examining the symmetry image-the more even the pattern, the better the symmetry
PROPORTION DIAGRAM
Each diamond is measured by an optical scanning device that captures a series of high resolution images and creates an exact 3D model of every facet and angle, providing accurate geometrical measurements of the diamond. This proportion diagram appears on your GCAL certificate.
- 6Optical Brilliance
Optical Brilliance
Gemprint
Gemprint® is a non-invasive, positive identification technology that records the unique optical 'fingerprint' of each diamond. Just like a human fingerprint, every diamond has a unique Gemprint. Capturing the unique Gemprint of your diamond in the initial processing stage, allows us to positively identify and track the diamond through our process. This optical fingerprint is captured and stored in GCAL's database for future verification and identification, and a digital image is printed on every GCAL Certificate.
How it works:
Gemprint uses a sophisticated system comprising laser technology, high resolution imaging, and automated positioning to direct a focused laser beam at the center of the diamond. The light enters the diamond and is broken into many rays as it reflects and refracts off the pavilion and crown facets. As the light reflects back out of the diamond, it creates a distinct Gemprint.
Laser Inscription
Laser Inscription quickly identifies a diamond and is included with this GCAL Guaranteed Diamond Grading Certificate. GCAL certified diamonds are laser inscribed with the unique certificate number assigned to the diamond. Photomicrographs, captured at more than 50x magnification, are taken to easily communicate what is inscribed on your diamond, and can be used as an additional piece of forensic identification of your diamond.
How it works:
GCAL uses a sophisticated IR laser technology specially designed for inscribing gemstones. When this laser is focused on a diamond's surface, it graphitizes a microscopic mark. A continuous series of these marks produces the numbers and letters you see on the girdle. The laser inscription mark is extremely shallow, only about 2-5 microns deep, less than one-tenth the width of the average human hair.
4Cs GRADING
WEIGHTS & MEASUREMENTS
Precise measurement of carat weight is important - slight differences can have a large impact on the value of a diamond. GCAL weighs diamonds on precise electronic balances according to international standards. This means that the weight is measured to the thousandth of a carat, and then is rounded to the hundredth of a carat. The electronic balances at GCAL are verified daily to ensure consistent and accurate results. The diamond is then measured by an optical scanning device that captures a series of high resolution images and creates an exact 3D model of every facet and angle, providing accurate geometrical measurements of the diamond. This proportion diagram appears on your GCAL certificate.
COLOR
Diamonds are color graded on a scale from D to Z. Each letter represents a slightly more saturated color. Your diamond is examined in a standard lighting environment and is compared to a set of Precision Master Color diamonds, which each have a precise color grade. Comparison of your diamond to the Precision Master diamonds continues until the color grade is determined. The difference between each color grade is very slight, but with experience, expert graders are able to consistently determine the accurate color grade of each diamond. GCAL utilizes a unique quality control procedure for grading the color and clarity of diamonds that assures the most accurate and consistent grading possible. At least three experienced gemologists examine and grade both the color and the clarity of every diamond. (After color grading, your diamond is checked for fluorescence, its reaction to ultraviolet light. A set of Master fluorescent diamonds is used to compare the strength of fluorescence. This intrinsic property is a permanent identifying characteristic of your diamond.)
CLARITY
Clarity is graded by examining your diamond under a microscope to assess internal and external characteristics such as crystals and feathers. A gemologist first inspects the diamond in the face-up position to find obvious inclusions. To find minute inclusions, the diamond has to be viewed through the pavilion as it is slowly rotated at least 3 full times, changing the viewing angle each time. The gemologist must assess the number, size, type, position and relief of each inclusion. After thorough inspection under the microscope, a 10x loupe is used to view the diamond in 4 different positions to determine the final clarity grade. GCAL utilizes a unique quality control procedure for grading the color and clarity of diamonds that assures the most accurate and consistent grading possible. At least three experienced gemologists examine and grade both the color and the clarity of every diamond.
RESEARCH
Before grading, every diamond is tested to confirm its origin - either natural earth mined or lab grown. If a diamond's origin cannot be verified by the initial spectroscopic analysis, then it is sent to the research department where additional more advanced tests are used to determine its authenticity. Considerable investment in state-of-the-art technologies has made GCAL one of the most well-equipped gem labs in the world. Once your diamond's origin is determined, it is ready for grading.
Photomicrograph
Photomicrographs are taken of the crown and pavilion of your diamond. These photos provide a forensic record of the exact appearance and condition of your diamond, and show internal and external characteristics visible at 10x magnification. Photographs are the most accurate way to illustrate the exact appearance and location of inclusions.
HEARTS & ARROWS
Hearts & Arrows is a term used to describe the patterns visible in perfectly faceted round brilliant cut diamonds when they are examined in specialized viewers. Through these viewers, it is possible to assess the alignment and consistency of every facet by looking at the equality of light return, or the hearts and arrows patterns.
A precisely faceted round brilliant diamond exhibits a pattern of eight arrows through the crown (top) side, and a pattern of eight hearts through the pavilion (bottom) side.
GCAL is the only laboratory that takes a real photograph of each diamond in the specialized viewer. This means that the images on your GCAL Certificate are actually of your diamond. Unlike the majority of the Hearts & Arrows photos printed on other lab reports or seen online, which are either generic sample images applied to every diamond or are computer generated - neither of which guarantees that the diamond you're paying a premium for is actually deserving of the term Hearts & Arrow.
OPTICAL BRILLIANCE
GCAL directly assesses the overall return of light to the viewer, called 'brilliance'.
The Optical Brilliance image is actually a digital photograph of the diamond taken in a special lighting environment that creates a strong contrast between the bright and dark areas. The image is then processed in a proprietary computer program that calculates the percentage of brilliance and the amount of light loss. This is a scientifically accurate and repeatable way to measure brilliance. The light gray areas of the image are facet outlines resulting from image processing to provide a realistic representation of the diamond's unique faceting.
In the Optical Brilliance Analysis image on the certificate, the white represents the light return and the blue represents areas of light loss. The light return is quantified based on measurable light return (aka - performance) and then graded as: Excellent, Very Good, Good, Fair or Poor.
Since the Optical Brilliance is measured by direct assessment, meaning that it is judged based on the way each diamond actually performs rather than a theoretical model, the brilliance image of each individual diamond will always look slightly different.
Brilliance is what gives a diamond its life, and what makes a diamond shine from across a room. Diamonds with a low percentage of brilliance look dull and dark.
OPTICAL SYMMETRY
The Optical Symmetry Analysis image is a digital photograph taken of each diamond in a special lighting environment that reveals the patterns of light return. All light returned at the same angles is represented by the same color. For example, all red areas represent light being returned within a consistent angle range. Therefore, the Optical Symmetry assesses the consistency of angles and alignment of facets by looking at the equality of light return.
Since the Optical Symmetry is measured by direct assessment, meaning that it is judged based on the way each diamond actually performs rather than a theoretical model, the symmetry images of each individual diamond will always look slightly different. Like the beauty and ever changing color patterns in a kaleidoscope, each diamond reveals its unique reflective pattern of symmetry. You can judge the cut of a diamond yourself simply by examining the symmetry image-the more even the pattern, the better the symmetry
PROPORTION DIAGRAM
Each diamond is measured by an optical scanning device that captures a series of high resolution images and creates an exact 3D model of every facet and angle, providing accurate geometrical measurements of the diamond. This proportion diagram appears on your GCAL certificate.
- 7Optical Symmetry
Optical Symmetry
Gemprint
Gemprint® is a non-invasive, positive identification technology that records the unique optical 'fingerprint' of each diamond. Just like a human fingerprint, every diamond has a unique Gemprint. Capturing the unique Gemprint of your diamond in the initial processing stage, allows us to positively identify and track the diamond through our process. This optical fingerprint is captured and stored in GCAL's database for future verification and identification, and a digital image is printed on every GCAL Certificate.
How it works:
Gemprint uses a sophisticated system comprising laser technology, high resolution imaging, and automated positioning to direct a focused laser beam at the center of the diamond. The light enters the diamond and is broken into many rays as it reflects and refracts off the pavilion and crown facets. As the light reflects back out of the diamond, it creates a distinct Gemprint.
Laser Inscription
Laser Inscription quickly identifies a diamond and is included with this GCAL Guaranteed Diamond Grading Certificate. GCAL certified diamonds are laser inscribed with the unique certificate number assigned to the diamond. Photomicrographs, captured at more than 50x magnification, are taken to easily communicate what is inscribed on your diamond, and can be used as an additional piece of forensic identification of your diamond.
How it works:
GCAL uses a sophisticated IR laser technology specially designed for inscribing gemstones. When this laser is focused on a diamond's surface, it graphitizes a microscopic mark. A continuous series of these marks produces the numbers and letters you see on the girdle. The laser inscription mark is extremely shallow, only about 2-5 microns deep, less than one-tenth the width of the average human hair.
4Cs GRADING
WEIGHTS & MEASUREMENTS
Precise measurement of carat weight is important - slight differences can have a large impact on the value of a diamond. GCAL weighs diamonds on precise electronic balances according to international standards. This means that the weight is measured to the thousandth of a carat, and then is rounded to the hundredth of a carat. The electronic balances at GCAL are verified daily to ensure consistent and accurate results. The diamond is then measured by an optical scanning device that captures a series of high resolution images and creates an exact 3D model of every facet and angle, providing accurate geometrical measurements of the diamond. This proportion diagram appears on your GCAL certificate.
COLOR
Diamonds are color graded on a scale from D to Z. Each letter represents a slightly more saturated color. Your diamond is examined in a standard lighting environment and is compared to a set of Precision Master Color diamonds, which each have a precise color grade. Comparison of your diamond to the Precision Master diamonds continues until the color grade is determined. The difference between each color grade is very slight, but with experience, expert graders are able to consistently determine the accurate color grade of each diamond. GCAL utilizes a unique quality control procedure for grading the color and clarity of diamonds that assures the most accurate and consistent grading possible. At least three experienced gemologists examine and grade both the color and the clarity of every diamond. (After color grading, your diamond is checked for fluorescence, its reaction to ultraviolet light. A set of Master fluorescent diamonds is used to compare the strength of fluorescence. This intrinsic property is a permanent identifying characteristic of your diamond.)
CLARITY
Clarity is graded by examining your diamond under a microscope to assess internal and external characteristics such as crystals and feathers. A gemologist first inspects the diamond in the face-up position to find obvious inclusions. To find minute inclusions, the diamond has to be viewed through the pavilion as it is slowly rotated at least 3 full times, changing the viewing angle each time. The gemologist must assess the number, size, type, position and relief of each inclusion. After thorough inspection under the microscope, a 10x loupe is used to view the diamond in 4 different positions to determine the final clarity grade. GCAL utilizes a unique quality control procedure for grading the color and clarity of diamonds that assures the most accurate and consistent grading possible. At least three experienced gemologists examine and grade both the color and the clarity of every diamond.
RESEARCH
Before grading, every diamond is tested to confirm its origin - either natural earth mined or lab grown. If a diamond's origin cannot be verified by the initial spectroscopic analysis, then it is sent to the research department where additional more advanced tests are used to determine its authenticity. Considerable investment in state-of-the-art technologies has made GCAL one of the most well-equipped gem labs in the world. Once your diamond's origin is determined, it is ready for grading.
Photomicrograph
Photomicrographs are taken of the crown and pavilion of your diamond. These photos provide a forensic record of the exact appearance and condition of your diamond, and show internal and external characteristics visible at 10x magnification. Photographs are the most accurate way to illustrate the exact appearance and location of inclusions.
HEARTS & ARROWS
Hearts & Arrows is a term used to describe the patterns visible in perfectly faceted round brilliant cut diamonds when they are examined in specialized viewers. Through these viewers, it is possible to assess the alignment and consistency of every facet by looking at the equality of light return, or the hearts and arrows patterns.
A precisely faceted round brilliant diamond exhibits a pattern of eight arrows through the crown (top) side, and a pattern of eight hearts through the pavilion (bottom) side.
GCAL is the only laboratory that takes a real photograph of each diamond in the specialized viewer. This means that the images on your GCAL Certificate are actually of your diamond. Unlike the majority of the Hearts & Arrows photos printed on other lab reports or seen online, which are either generic sample images applied to every diamond or are computer generated - neither of which guarantees that the diamond you're paying a premium for is actually deserving of the term Hearts & Arrow.
OPTICAL BRILLIANCE
GCAL directly assesses the overall return of light to the viewer, called 'brilliance'.
The Optical Brilliance image is actually a digital photograph of the diamond taken in a special lighting environment that creates a strong contrast between the bright and dark areas. The image is then processed in a proprietary computer program that calculates the percentage of brilliance and the amount of light loss. This is a scientifically accurate and repeatable way to measure brilliance. The light gray areas of the image are facet outlines resulting from image processing to provide a realistic representation of the diamond's unique faceting.
In the Optical Brilliance Analysis image on the certificate, the white represents the light return and the blue represents areas of light loss. The light return is quantified based on measurable light return (aka - performance) and then graded as: Excellent, Very Good, Good, Fair or Poor.
Since the Optical Brilliance is measured by direct assessment, meaning that it is judged based on the way each diamond actually performs rather than a theoretical model, the brilliance image of each individual diamond will always look slightly different.
Brilliance is what gives a diamond its life, and what makes a diamond shine from across a room. Diamonds with a low percentage of brilliance look dull and dark.
OPTICAL SYMMETRY
The Optical Symmetry Analysis image is a digital photograph taken of each diamond in a special lighting environment that reveals the patterns of light return. All light returned at the same angles is represented by the same color. For example, all red areas represent light being returned within a consistent angle range. Therefore, the Optical Symmetry assesses the consistency of angles and alignment of facets by looking at the equality of light return.
Since the Optical Symmetry is measured by direct assessment, meaning that it is judged based on the way each diamond actually performs rather than a theoretical model, the symmetry images of each individual diamond will always look slightly different. Like the beauty and ever changing color patterns in a kaleidoscope, each diamond reveals its unique reflective pattern of symmetry. You can judge the cut of a diamond yourself simply by examining the symmetry image-the more even the pattern, the better the symmetry
PROPORTION DIAGRAM
Each diamond is measured by an optical scanning device that captures a series of high resolution images and creates an exact 3D model of every facet and angle, providing accurate geometrical measurements of the diamond. This proportion diagram appears on your GCAL certificate.
- 8Proportion Diagram
Proportion Diagram
Gemprint
Gemprint® is a non-invasive, positive identification technology that records the unique optical 'fingerprint' of each diamond. Just like a human fingerprint, every diamond has a unique Gemprint. Capturing the unique Gemprint of your diamond in the initial processing stage, allows us to positively identify and track the diamond through our process. This optical fingerprint is captured and stored in GCAL's database for future verification and identification, and a digital image is printed on every GCAL Certificate.
How it works:
Gemprint uses a sophisticated system comprising laser technology, high resolution imaging, and automated positioning to direct a focused laser beam at the center of the diamond. The light enters the diamond and is broken into many rays as it reflects and refracts off the pavilion and crown facets. As the light reflects back out of the diamond, it creates a distinct Gemprint.
Laser Inscription
Laser Inscription quickly identifies a diamond and is included with this GCAL Guaranteed Diamond Grading Certificate. GCAL certified diamonds are laser inscribed with the unique certificate number assigned to the diamond. Photomicrographs, captured at more than 50x magnification, are taken to easily communicate what is inscribed on your diamond, and can be used as an additional piece of forensic identification of your diamond.
How it works:
GCAL uses a sophisticated IR laser technology specially designed for inscribing gemstones. When this laser is focused on a diamond's surface, it graphitizes a microscopic mark. A continuous series of these marks produces the numbers and letters you see on the girdle. The laser inscription mark is extremely shallow, only about 2-5 microns deep, less than one-tenth the width of the average human hair.
4Cs GRADING
WEIGHTS & MEASUREMENTS
Precise measurement of carat weight is important - slight differences can have a large impact on the value of a diamond. GCAL weighs diamonds on precise electronic balances according to international standards. This means that the weight is measured to the thousandth of a carat, and then is rounded to the hundredth of a carat. The electronic balances at GCAL are verified daily to ensure consistent and accurate results. The diamond is then measured by an optical scanning device that captures a series of high resolution images and creates an exact 3D model of every facet and angle, providing accurate geometrical measurements of the diamond. This proportion diagram appears on your GCAL certificate.
COLOR
Diamonds are color graded on a scale from D to Z. Each letter represents a slightly more saturated color. Your diamond is examined in a standard lighting environment and is compared to a set of Precision Master Color diamonds, which each have a precise color grade. Comparison of your diamond to the Precision Master diamonds continues until the color grade is determined. The difference between each color grade is very slight, but with experience, expert graders are able to consistently determine the accurate color grade of each diamond. GCAL utilizes a unique quality control procedure for grading the color and clarity of diamonds that assures the most accurate and consistent grading possible. At least three experienced gemologists examine and grade both the color and the clarity of every diamond. (After color grading, your diamond is checked for fluorescence, its reaction to ultraviolet light. A set of Master fluorescent diamonds is used to compare the strength of fluorescence. This intrinsic property is a permanent identifying characteristic of your diamond.)
CLARITY
Clarity is graded by examining your diamond under a microscope to assess internal and external characteristics such as crystals and feathers. A gemologist first inspects the diamond in the face-up position to find obvious inclusions. To find minute inclusions, the diamond has to be viewed through the pavilion as it is slowly rotated at least 3 full times, changing the viewing angle each time. The gemologist must assess the number, size, type, position and relief of each inclusion. After thorough inspection under the microscope, a 10x loupe is used to view the diamond in 4 different positions to determine the final clarity grade. GCAL utilizes a unique quality control procedure for grading the color and clarity of diamonds that assures the most accurate and consistent grading possible. At least three experienced gemologists examine and grade both the color and the clarity of every diamond.
RESEARCH
Before grading, every diamond is tested to confirm its origin - either natural earth mined or lab grown. If a diamond's origin cannot be verified by the initial spectroscopic analysis, then it is sent to the research department where additional more advanced tests are used to determine its authenticity. Considerable investment in state-of-the-art technologies has made GCAL one of the most well-equipped gem labs in the world. Once your diamond's origin is determined, it is ready for grading.
Photomicrograph
Photomicrographs are taken of the crown and pavilion of your diamond. These photos provide a forensic record of the exact appearance and condition of your diamond, and show internal and external characteristics visible at 10x magnification. Photographs are the most accurate way to illustrate the exact appearance and location of inclusions.
HEARTS & ARROWS
Hearts & Arrows is a term used to describe the patterns visible in perfectly faceted round brilliant cut diamonds when they are examined in specialized viewers. Through these viewers, it is possible to assess the alignment and consistency of every facet by looking at the equality of light return, or the hearts and arrows patterns.
A precisely faceted round brilliant diamond exhibits a pattern of eight arrows through the crown (top) side, and a pattern of eight hearts through the pavilion (bottom) side.
GCAL is the only laboratory that takes a real photograph of each diamond in the specialized viewer. This means that the images on your GCAL Certificate are actually of your diamond. Unlike the majority of the Hearts & Arrows photos printed on other lab reports or seen online, which are either generic sample images applied to every diamond or are computer generated - neither of which guarantees that the diamond you're paying a premium for is actually deserving of the term Hearts & Arrow.
OPTICAL BRILLIANCE
GCAL directly assesses the overall return of light to the viewer, called 'brilliance'.
The Optical Brilliance image is actually a digital photograph of the diamond taken in a special lighting environment that creates a strong contrast between the bright and dark areas. The image is then processed in a proprietary computer program that calculates the percentage of brilliance and the amount of light loss. This is a scientifically accurate and repeatable way to measure brilliance. The light gray areas of the image are facet outlines resulting from image processing to provide a realistic representation of the diamond's unique faceting.
In the Optical Brilliance Analysis image on the certificate, the white represents the light return and the blue represents areas of light loss. The light return is quantified based on measurable light return (aka - performance) and then graded as: Excellent, Very Good, Good, Fair or Poor.
Since the Optical Brilliance is measured by direct assessment, meaning that it is judged based on the way each diamond actually performs rather than a theoretical model, the brilliance image of each individual diamond will always look slightly different.
Brilliance is what gives a diamond its life, and what makes a diamond shine from across a room. Diamonds with a low percentage of brilliance look dull and dark.
OPTICAL SYMMETRY
The Optical Symmetry Analysis image is a digital photograph taken of each diamond in a special lighting environment that reveals the patterns of light return. All light returned at the same angles is represented by the same color. For example, all red areas represent light being returned within a consistent angle range. Therefore, the Optical Symmetry assesses the consistency of angles and alignment of facets by looking at the equality of light return.
Since the Optical Symmetry is measured by direct assessment, meaning that it is judged based on the way each diamond actually performs rather than a theoretical model, the symmetry images of each individual diamond will always look slightly different. Like the beauty and ever changing color patterns in a kaleidoscope, each diamond reveals its unique reflective pattern of symmetry. You can judge the cut of a diamond yourself simply by examining the symmetry image-the more even the pattern, the better the symmetry
PROPORTION DIAGRAM
Each diamond is measured by an optical scanning device that captures a series of high resolution images and creates an exact 3D model of every facet and angle, providing accurate geometrical measurements of the diamond. This proportion diagram appears on your GCAL certificate.